-
-
-
B-23, Sector-63, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301




B-23, Sector-63, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301


Enterprise Resource Planning software help organizations centralize their database and use it for decision making. It is essential that the data is protected from unauthorized access and distribution. ERPs achieve this through Roles and access rights.
Access rights define what data can be accessed, created or edited by a person and what tasks the person can perform. ERPs have defined functions that can be performed in each functional area. Roles are created around tasks a person would perform. For example, an accountant may have right to create new transactions, view those transactions and access data related to bank accounts etc. The person would be accessing data or adding to the data in finance and accounts module only. A person who performs function of material resource planning would create production plan, assess material shortages and create purchase indents. To perform the function, the person would need access to data in production, procurement and inventory module. A typical roles and function chart may look like this
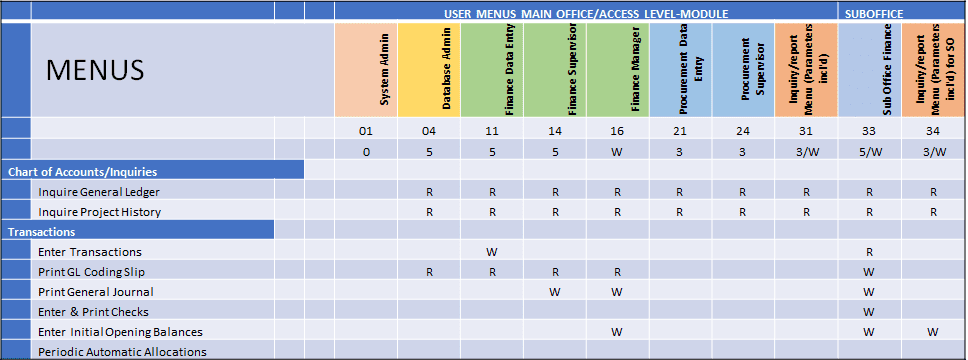
The ERPs create standard roles with access rights. These can be customized to suit the requirements of the customers. ERP companies also create license requirements around it. There are full access licenses that provide complete access either to a functional area or across functional areas. For example,
The accountant has data entry rights along with view rights to see transactions, view and print transactions. The accountant may not be able to view and/or print trial balance and account schedules. The supervisor of the accountant, would not be able to write the transactions but would be able to review them and post them after corrections. That is if the supervisor finds an error in the transaction, he can correct it and then post it. Posting is basically a process where the transactions get added to the database from the temporary day book. A finance manager, unlike finance supervisor can not only post transactions but can also print trial balance, account schedule and setup opening balances for the start of fiscal year or fiscal period. If the company has a regional office or a branch office, the accountant in the branch will be able to write transactions, print checks, see the trial balance and account schedules for his branch.
The key issue to be considered while designing roles in ERPs is Segregation of Duties. That is a system of checks and balance where each process or task is broken into sub tasks and allocated to different persons so as to prevent fraud. For example, chances of frauds increase if the person who is writing transactions also has responsibility of conducting bank reconciliations. It is a good practice to allocate responsibility of Bank reconciliations to a person who does not write or post transactions in the system. Another example is that person managing stores and purchase should not be the same. Somehow because of convenience, most founders or owners find it easy to assign both the responsibilities to the same person. We, as ERP consultants find it very often.
Thus a company cannot club functions and develop what access it would want to provide and define it as a role. The roles for a position can change over a period of time based on how the organization grows. Similar roles are developed in all functional areas, such as procurement, inventory, sales, etc. If you want to keep your data safe, do pay attention to how roles are defined in your ERP. Happy hunting.